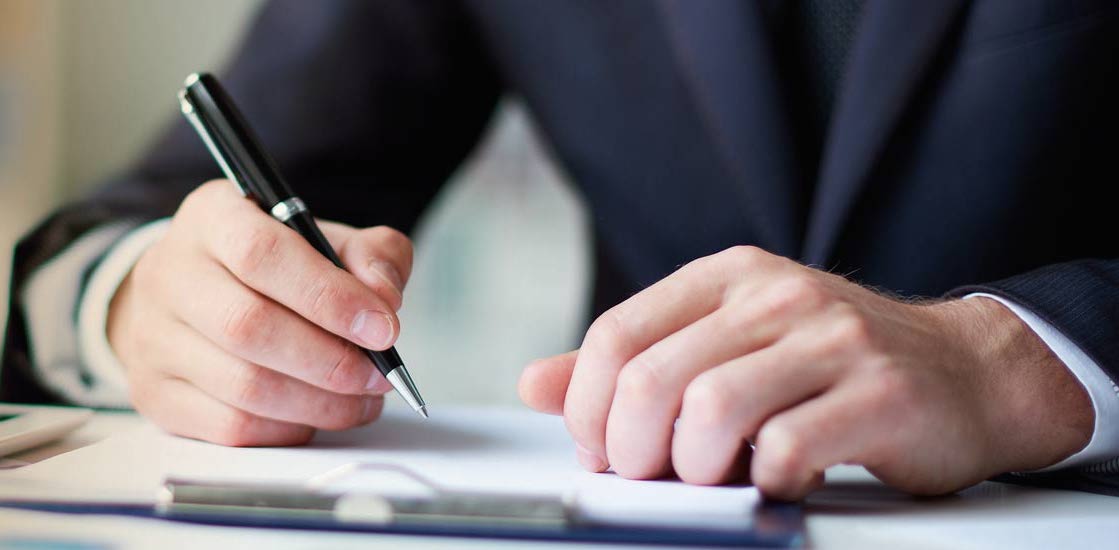
In India there are different laws for property distribution. Basically below laws apply to the distribution of property:-
Shriya law For Muslim Property Distribution:-
The Muslim laws of inheritance require at least 2/3 of the deceased’s property to go by line of succession to his family and allow up to 1/3 to be settled by testamentary succession. But as there was no will here, the property bequeathed will go to the man’s heirs in absence of a will by him.
For Hindus there is Hindu Succession Act 1956 for Property distribution:-
1. If the Deceased is a Male
The property of a Hindu male dying intestate, or without a will, would be given first to heirs within Class I. If there are no heirs categorized as Class I, the property will be given to heirs within Class II. If there are no Class I or II heirs, then the property will first go to agnates (distant blood relatives of male lineage) and if no agnates are available then to cognates (distant blood
relatives of male or female lineage). And if there are no cognates then the estate will go to the government. To know the members of Class I & II please refer the schedule given in Hindu Succession Act 1956
2. If the Deceased is a Female
The property of a female Hindu dying without a will shall devolve according to the following rules:
(a) firstly, upon the sons and daughters (including the children of any pre-deceased son or
daughter) and the husband;
(b) secondly, upon the heirs of the husband;
(c) thirdly, upon the mother and father;
(d) fourthly, upon the heirs of the father; and
(e) lastly, upon the heirs of the mother.
In case of a Hindu female dying intestate and without any issue or any children or any predeceased children, any property inherited by her from her parents shall not devolve upon her husband or his heirs but revert to her natal family.
Similarly, in case a Hindu female dies intestate and without any issue or any children or any predeceased children, then any property inherited by her from her husband or her father-in-law devolves upon the heirs of her husband. Thus, property inherited from her husband would not devolve upon her father or his heirs